Introduction
Mankind has always looked for ways to improve productivity and make work more efficient. From the steam engine and electricity to assembly lines, computers, and now AI, every major breakthrough increased output and pushed society toward higher prosperity. Each wave reduced friction in how value is created.
Early technologies still depended heavily on human labor. The steam engine needed operators, factories needed workers, and even computers required humans at every critical step. These tools amplified labor, but they never truly replaced it. Productivity scaled, but manpower remained essential.
AI breaks that pattern. For the first time, software can build software. Code can be written, tested, and improved by machines themselves, showing that cognitive labor is no longer the main constraint on growth.
So far, this shift has mostly impacted white collar work. Programming, design, research, coordination. While output in the digital world is accelerating fast, physical production has not kept pace, and the demand for physical goods and services continues to rise. Housing, food, logistics, manufacturing, healthcare. This growing gap between digital productivity and physical output is becoming impossible to ignore.
That gap is where robotics comes in.
Robotics Today
Robots have long existed across industrial, medical, logistics, and aerospace environments. What has changed is not just their capability, but their proximity to everyday life. Robotics is moving out of controlled settings and into human spaces, including homes.
Humanoid form matters because the physical world is already optimized for humans. Doors, tools, stairs, warehouses, hospitals. Instead of rebuilding infrastructure, companies are building robots that can operate inside existing environments. This makes humanoids the fastest path from prototype to real world deployment.
Humanoid robotics is improving exponentially, and this was clearly showcased at CES 2026. What stood out was not just better demos, but faster iteration across locomotion, manipulation, and autonomy. Progress is no longer linear, it is exponential.
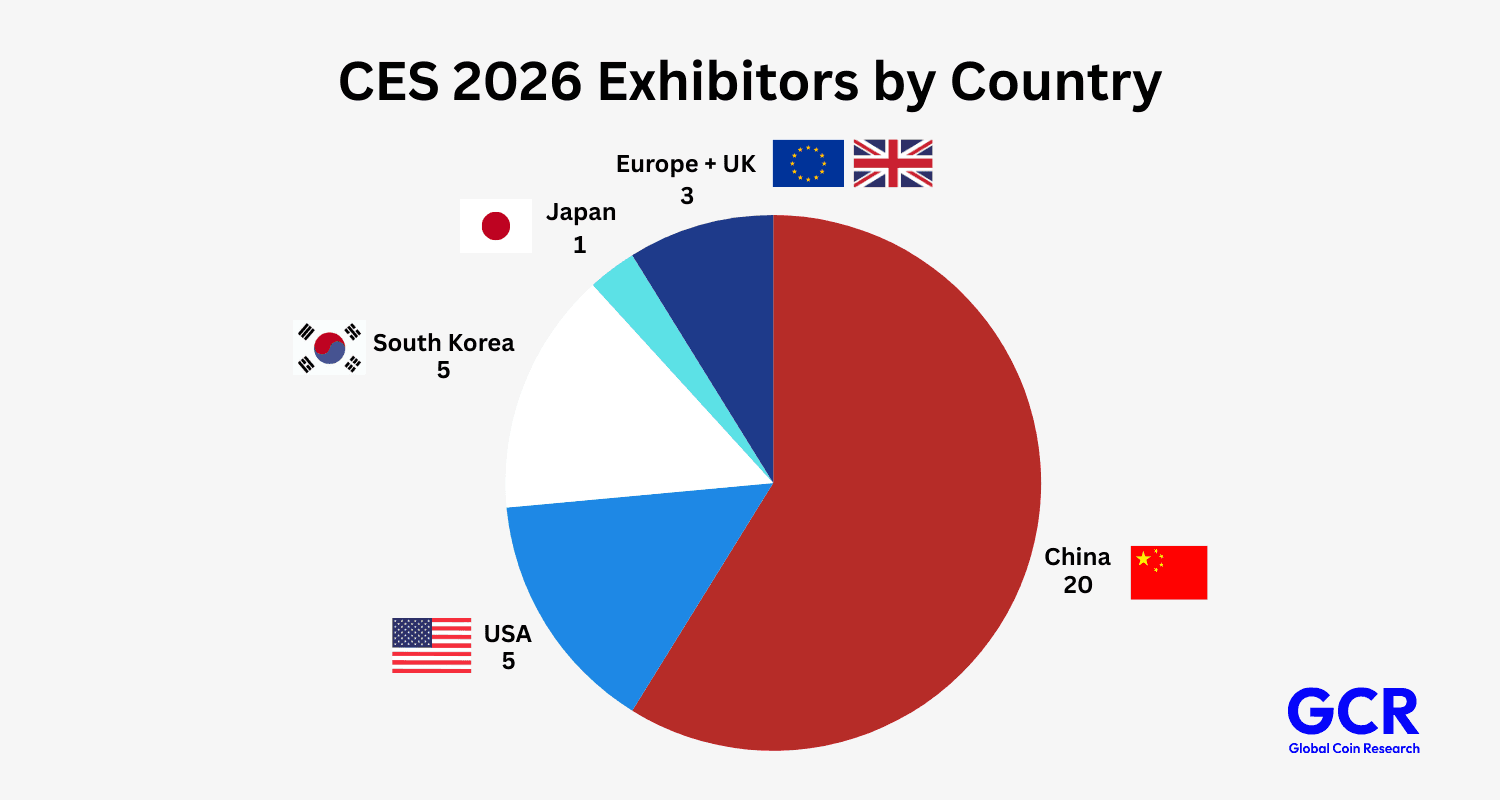
Source: CyberRobo
Adding AI into the equation changes the trajectory entirely. Robots are starting to learn from their own experience, refining movement, balance, and task execution without constant human supervision. With more deployments, more data, and rapidly improving AI intelligence, feedback loops tighten. The more robots exist, the faster robotics advances.
The robotics sector is also becoming a strategic priority at the national level. Governments increasingly view humanoid robotics as core infrastructure tied to productivity, resilience, and long term economic power. Robotics is no longer just a commercial race, but a geopolitical one.
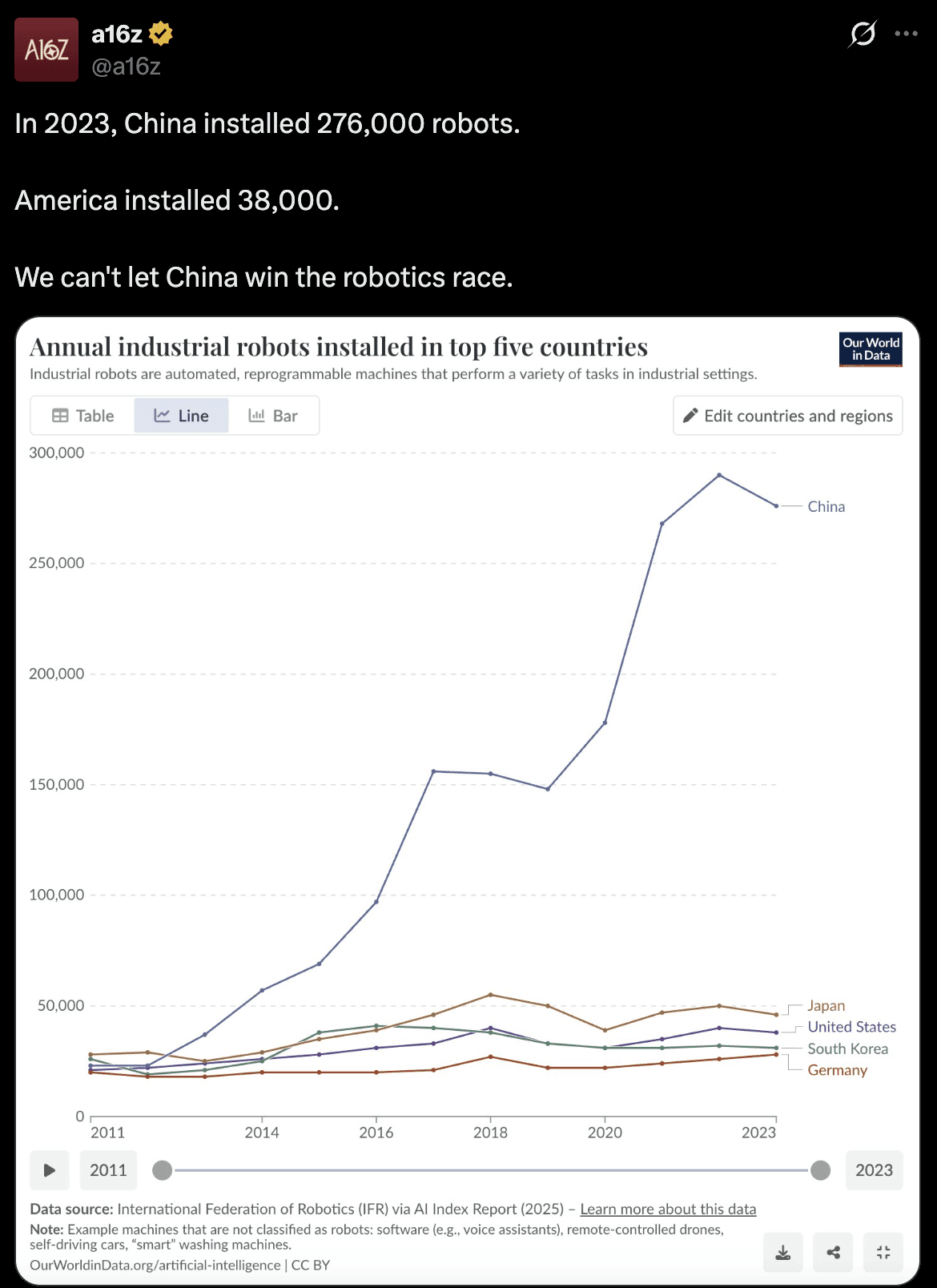
Source: a16z
According to Counterpoint Research, around 16,000 humanoid robots were installed globally in 2025, with China accounting for more than 80 percent of those deployments. This early concentration highlights how aggressively China is pushing humanoid robotics into real world use cases. Adoption is already uneven and strategically driven.

Source: The Chosun
Looking further ahead, Morgan Stanley estimates that by 2050 around 90 percent of humanoid robots, roughly 930 million units, will be used for repetitive, simple, and structured work, primarily across industrial and commercial sectors. China is projected to lead with approximately 302.3 million humanoids in use, followed by the United States at around 77.7 million.
The economic impact is much closer than it appears. According to McKinsey & Company, by 2030 up to $2.9 trillion in economic value could be unlocked in the United States alone if organizations redesign workflows around people, AI agents, and robots working together rather than automating individual tasks in isolation.
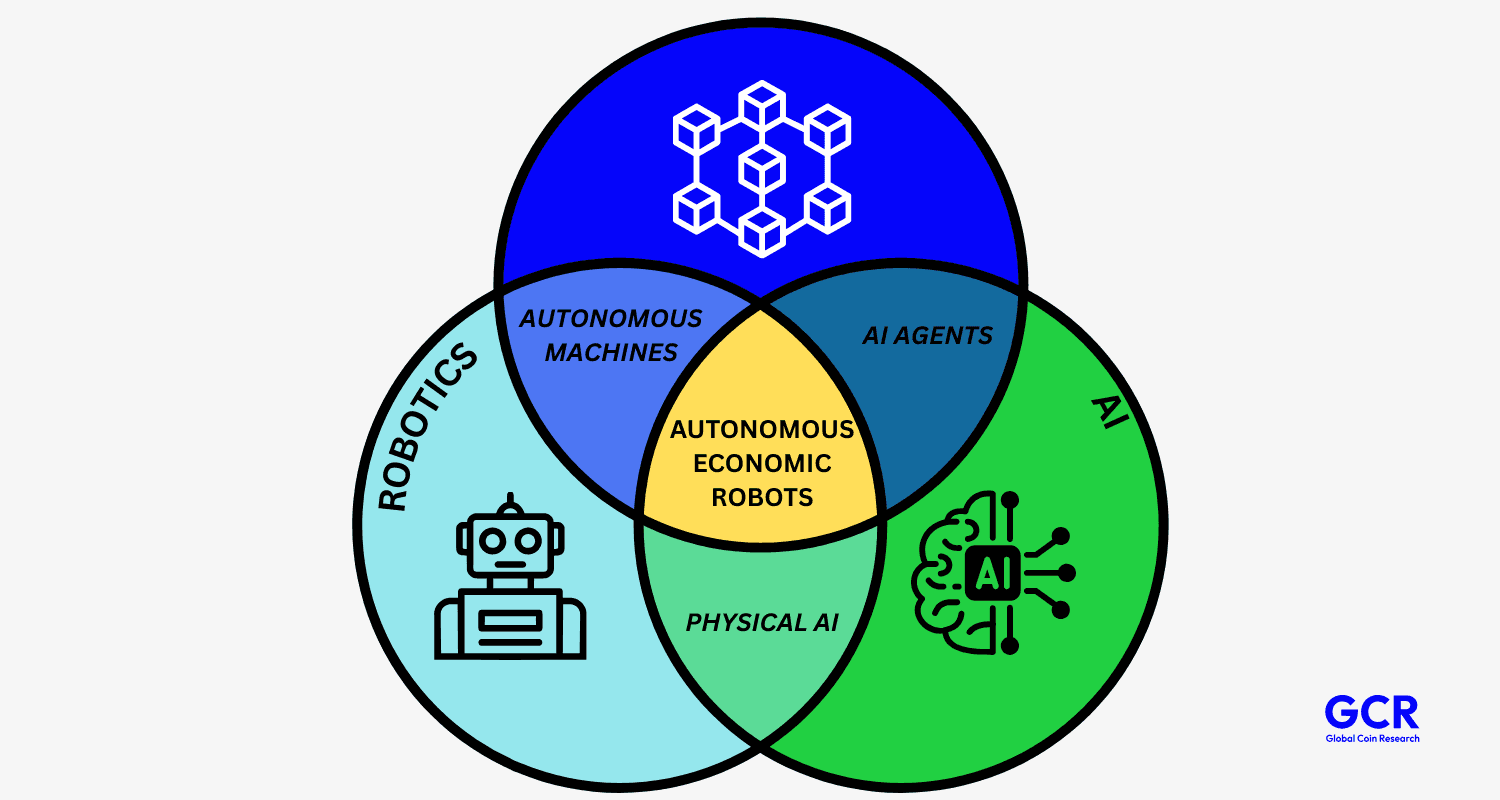
Robotics x Crypto
Today, crypto is still largely viewed as a financial instrument. Trading, speculation, payments, and stores of value dominate the narrative. But the underlying technology was never limited to finance.
Blockchain and crypto introduce a new coordination layer for the digital and physical world. As robotics scales, this layer becomes increasingly important. Robots will need to transact, own resources, share data, and operate across borders without relying on traditional financial and legal systems.
Crypto provides the infrastructure that allows robotics to function at scale.
Machine to Machine Payments
Robots operate continuously and transact far more frequently than humans. Crypto enables instant micro payments between machines without banks, invoices, or settlement delays. This is essential once robots start buying services, energy, or tasks autonomously.
Robots as Onchain Economic Agents
Robots will not just execute tasks, they will participate in the economy. Being onchain allows robots to receive payments, hold balances, and interact with smart contracts directly. This turns robots from tools into autonomous economic actors.
Web3 Native Wallets Instead of Traditional Bank Accounts
Traditional finance was not built for machines. Web3 wallets allow robots to open accounts instantly, globally, and without permission. This removes friction and enables deployment across borders from day one.
Tokenized Ownership of Robots and Fleets
Robotics is capital intensive and slow to finance through traditional models. Tokenization allows shared ownership, revenue distribution, and liquidity for robotic assets. Investors can fund robots the same way they fund digital infrastructure.
Blockchain Based Data Distribution for Machine Learning
Robots generate massive amounts of real world data. Blockchain enables transparent ownership, controlled sharing, and monetization of that data. Better data access leads to faster training and more capable machines.
Decentralization and Privacy
As robots move into homes, hospitals, and workplaces, they will handle sensitive data. Healthcare records, behavioral data, and physical environments cannot be controlled by a single central entity. Decentralized systems reduce concentration risk and give users control over access and data usage. Crypto enables verifiable rules and privacy preserving coordination, which is critical for trust and adoption.
Projects to Keep an Eye on
The robotics segment has not yet received the spotlight it deserves. Most attention still flows toward software and pure AI narratives, while physical automation quietly compounds in the background.
As humanoid robotics, AI, and crypto infrastructure begin to converge, the narrative is starting to shift. Below are some of the projects that caught our attention within the emerging robotics landscape.
PrismaX - Teleoperation as a Learning Engine
PrismaX positions itself as a service layer for real world AI robotics, using teleoperation to convert human interaction into high quality training data that compounds into better models and more capable robots. Users remotely control robots directly to perform simple pick and place tasks, with every interaction feeding into robotics data collection used to train autonomous systems. Human input becomes the bridge between today’s robots and full autonomy, turning learning from a lab constrained process into a scalable and distributed one.
Why this matters
Robots perform well in ideal and controlled environments. Scaling them into the real world requires exposure to uncertainty, edge cases, and imperfect conditions. Large diverse datasets are essential if robots are expected to operate reliably in unknown environments.
Auki - A Map for AI
Auki is building what can be described as a map for AI. At its core is the posemesh, a decentralized machine perception network that allows robots, smart glasses, and other devices to securely and privately share spatial data and computing power. This enables machines to form a shared understanding of the physical world.
By creating a real world web, Auki makes physical locations browsable, navigable, and searchable for AI systems. Robots and digital devices can coordinate in the same space without relying on centralized control, while a token based economy enables exchange of spatial data and compute resources. The physical world becomes machine readable.
Why this matters
Around 70 percent of the global economy is still tied to physical locations and labor. Making the physical world accessible to AI is critical for scaling robotics, automation, and real world applications beyond digital environments.
GEODNET - Positioning Network for an Autonomous Future
GEODNET is building a Real Time Kinematics network that delivers centimeter level positioning accuracy. Recognized by Grayscale as an asset under consideration, GEODNET takes a decentralized approach where users run satellite reference stations that earn crypto rewards while powering real world infrastructure. Participants do not just earn passive income, they contribute to precision navigation at scale.
The network supports critical use cases such as AI driven robots, drones, autonomous vehicles, augmented reality, and metaverse applications, providing the spatial and timing infrastructure these systems depend on.
Why this matters
Centimeter level positioning accuracy and nanosecond level time precision are essential for autonomous systems. As robots and machines increasingly operate independently in the physical world, reliable positioning becomes foundational infrastructure.
Peaq - Economic Layer for Robots
Peaq serves as the economic system and coordination layer for the machine economy. It is a blockchain optimized for machines, robots, and autonomous agents, providing native standards for identity, ownership, time, access control, and payments. This allows devices to participate in the economy without relying on human intermediaries.
On peaq, users can co own robots that perform work, generate revenue, and automatically distribute earnings to their owners. Robots become productive assets rather than fixed costs, and coordination happens at the protocol level.
Why this matters
Robots need a native economic layer to scale. peaq provides the infrastructure that enables ownership, incentives, and coordination for machines operating autonomously in the real world.
IoTeX - Onchain Identity Layer
IoTeX is building blockchain infrastructure that connects AI systems with the physical world. As AI moves beyond purely digital environments, its effectiveness increasingly depends on access to live and trustworthy real world data. IoTeX addresses this through Realms, domain specific knowledge bases that aggregate real time data from machines, sensors, and people to generate actionable intelligence across mobility, health, energy, and robotics.
Another core component is ioID, an onchain identity layer for machines and AI agents. Each ioID is a globally unique identifier paired with an onchain wallet, enabling discovery, economic autonomy, and trusted interactions between machines, agents, and AI systems. This turns machines into verifiable participants in the Physical AI economy.
Why this matters
Humanoid robots face complex tasks that demand mobility, perception, adaptability, and continuous learning. Realms address this by providing continuously updated, real world data and domain specific intelligence that robots and AI systems can rely on to operate beyond controlled environments. Combined with ioID, this enables robots to be identifiable, trusted, and economically active as first class participants in the Physical AI economy.
Conclusion
Despite ongoing challenges around learning, mobility, adaptation to real world environments, cost, and unresolved legal frameworks, one trend is clear. Robotics will become a fundamental part of everyday life. Homes, workplaces, logistics, healthcare, and cities will increasingly rely on autonomous machines.
For robots to operate at scale, they will need more than intelligence and hardware. They will need identity, payments, coordination, and trust across borders and institutions. This is where crypto becomes essential, not optional.
Robotics executes in the physical world. Crypto coordinates in the economic one.